The Future of Farming: How Tidal Seedbeds Are Revolutionizing Agriculture
As the global population grows and arable land shrinks, innovative farming techniques are becoming essential to sustainable food production. One such breakthrough is tidal seedbed technology—an efficient, water-saving method that’s transforming how we grow crops.
What Is a Tidal Seedbed?
A tidal seedbed (or flood-and-drain system) is a hydroponic-based growing platform where plants are periodically flooded with nutrient-rich water and then drained. This mimics natural tidal movements, ensuring optimal oxygenation and nutrient absorption for seedlings.
Key Benefits
Water Efficiency – Uses up to 70% less water than traditional irrigation by recycling the nutrient solution.
Faster Growth – Enhanced root aeration boosts plant metabolism, accelerating growth rates by 20-30%.
Space-Saving – Ideal for urban farming, greenhouses, and vertical farms due to compact design.
Reduced Disease Risk – Controlled flooding minimizes soil-borne pathogens and algae buildup.
How It Works
Flood Phase – The tray fills with water/nutrients, allowing roots to absorb essentials.
Drain Phase – Gravity drains the solution back into a reservoir, pulling fresh oxygen to the roots.
Automation – Timers or sensors regulate cycles (typically 4-6 floods per day).
Applications
Commercial Nurseries – Uniform seedling production for vegetables (lettuce, herbs, tomatoes).
Research Labs – Studying plant responses to nutrients/hydroponics.
Home Growers – Compact systems for balcony gardening.
Challenges & Solutions
Initial Cost – Higher setup investment than soil beds (offset by long-term water/pesticide savings).
Power Dependency – Requires pumps/timers (solar-powered options now available).
The Future
With advances in AI-controlled irrigation and sustainable materials, tidal seedbeds could become a cornerstone of climate-resilient farming.

The Future of Farming: Hydroponics and Sustainable Agriculture
Introduction
Hydroponics, the practice of growing plants without soil, is revolutionizing the way we think about agriculture. By using nutrient-rich water solutions, hydroponics allows plants to grow faster, use fewer resources, and thrive in environments where traditional farming is impossible. As the global population grows and arable land becomes scarce, hydroponics offers a sustainable solution to meet the world’s food demands.
How Hydroponics Works
In hydroponic systems, plants are grown in inert mediums like perlite, coconut coir, or clay pellets, which provide support while allowing roots to access oxygen and nutrients. Nutrient solutions are carefully balanced to deliver essential minerals directly to the roots, ensuring optimal growth. Common hydroponic systems include:
-
Deep Water Culture (DWC): Plants float on water with roots submerged in nutrient-rich solutions.
-
Nutrient Film Technique (NFT): A thin film of nutrient solution flows over the roots.
-
Ebb and Flow: Plants are periodically flooded with nutrient solutions and then drained.

Benefits of Hydroponics
-
Water Efficiency: Hydroponics uses up to 90% less water than traditional farming, as water is recirculated within the system.
-
Space Savings: Vertical hydroponic systems maximize space, making them ideal for urban farming.
-
Faster Growth: Plants grow 30-50% faster due to direct access to nutrients and oxygen.
-
Year-Round Production: Controlled environments allow for continuous growing cycles, regardless of weather conditions.
-
Reduced Pesticides: Soil-free systems minimize pests and diseases, reducing the need for chemical treatments.
Challenges and Solutions
While hydroponics offers many advantages, it also presents challenges such as high initial costs, technical expertise requirements, and energy consumption for lighting and climate control. However, advancements in technology, such as energy-efficient LED lights and automated monitoring systems, are making hydroponics more accessible and cost-effective.
Conclusion
Hydroponics is not just a farming method; it’s a movement toward sustainable agriculture. By reducing resource consumption, increasing yields, and enabling farming in urban areas, hydroponics has the potential to transform global food systems and ensure food security for future generations.
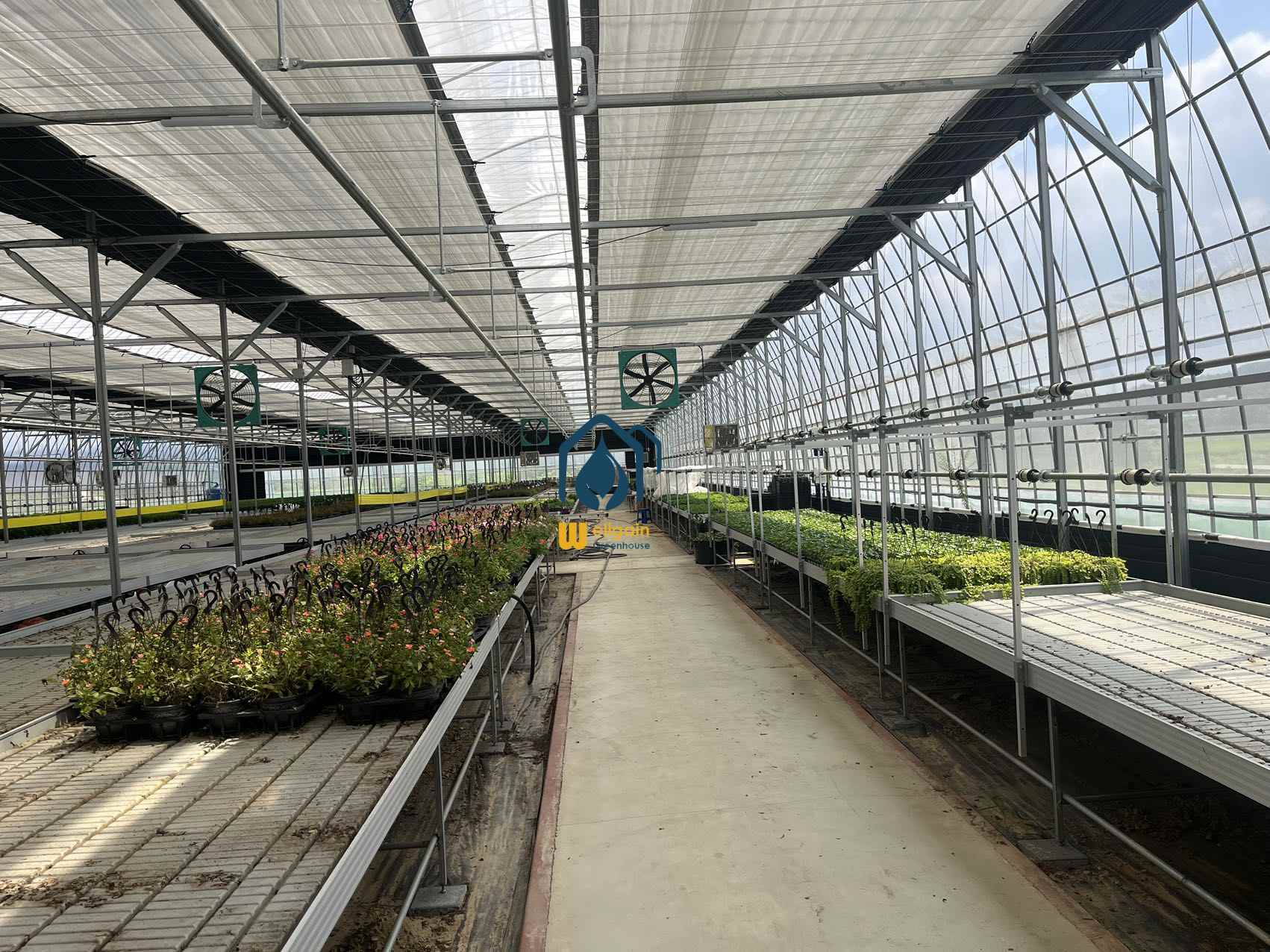
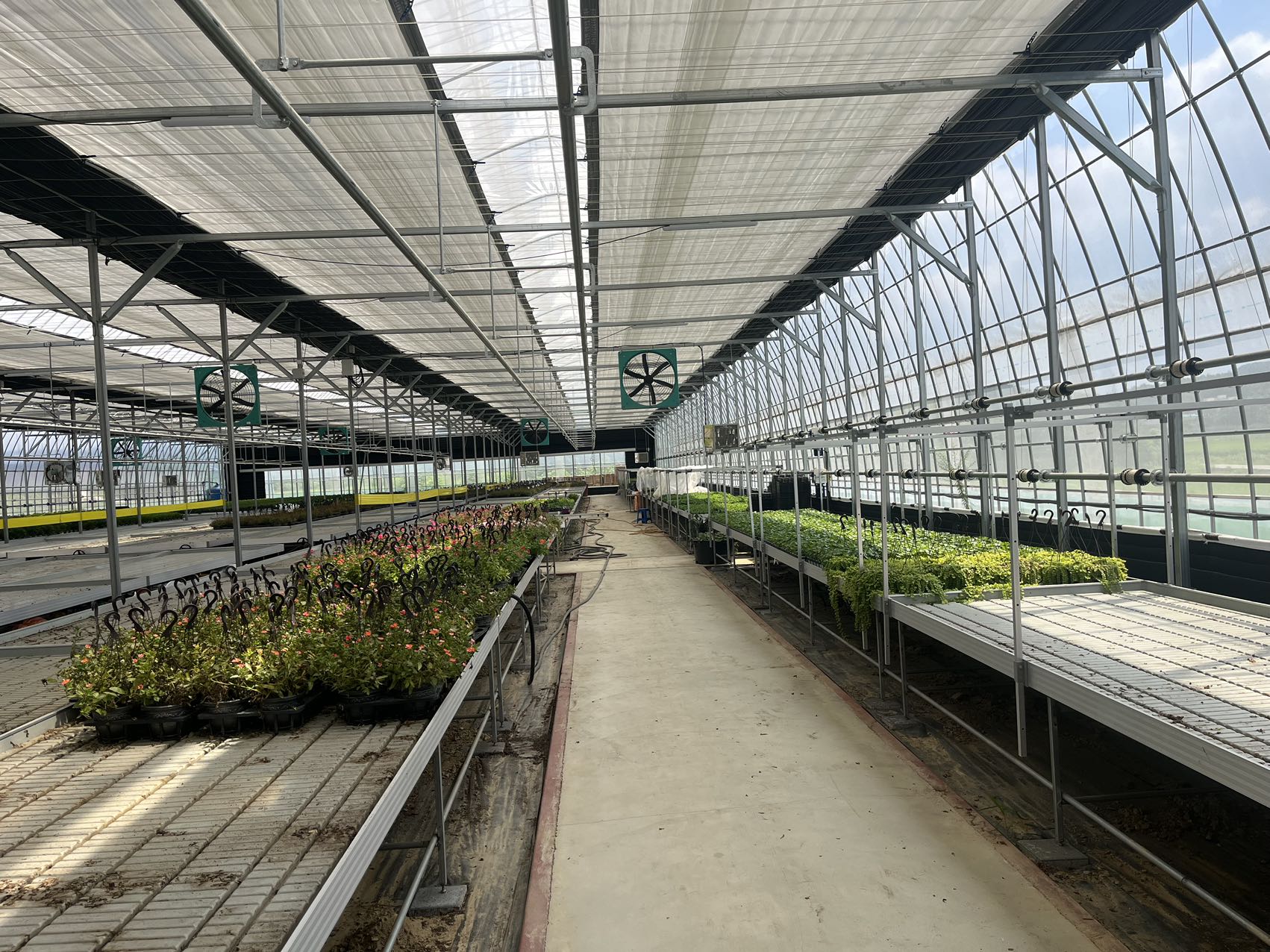
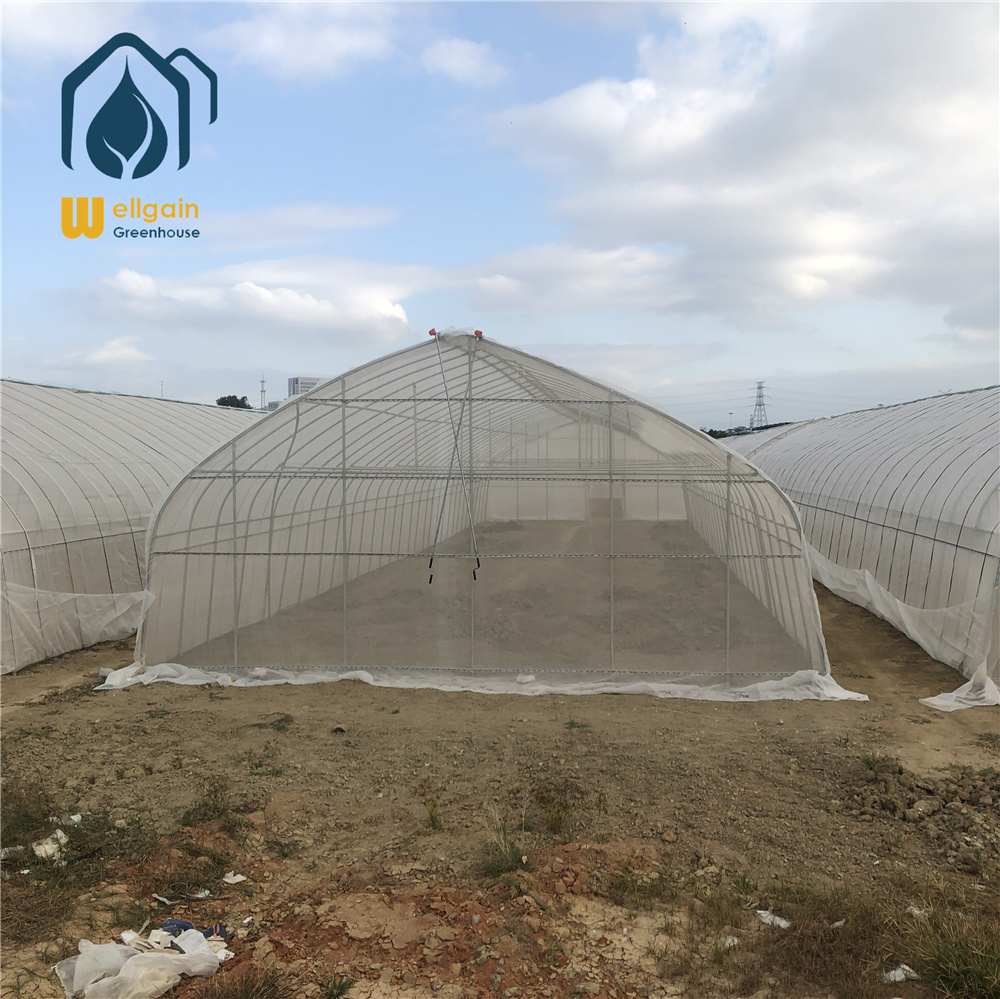
TU Film Greenhouses in Modern Agriculture
Introduction
TU film greenhouses, also known as tunnel greenhouses or polytunnels, are a popular and cost-effective solution for modern agriculture. These structures, made of polyethylene film stretched over a metal or PVC frame, provide a controlled environment for crop cultivation. With their versatility, affordability, and efficiency, TU film greenhouses are widely used by farmers and gardeners to extend growing seasons, protect crops, and increase yields.
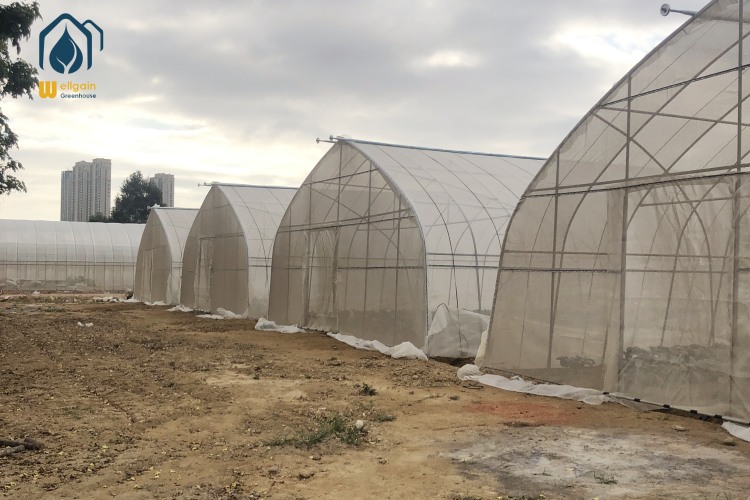

Key Features of TU Film Greenhouses
-
Cost-Effective: TU film greenhouses are significantly cheaper to build and maintain compared to glass or polycarbonate greenhouses, making them accessible to small-scale farmers.
-
Light Transmission: The polyethylene film provides excellent light diffusion, ensuring uniform light distribution for optimal plant growth.
-
Durability: Modern UV-resistant films can last 3-5 years, withstanding moderate weather conditions like wind, rain, and light snow.
-
Versatility: TU film greenhouses can be used for growing a wide range of crops, including vegetables, fruits, flowers, and seedlings.
-
Energy Efficiency: The film retains heat effectively, reducing the need for additional heating in colder climates.
Drain-to-Waste System:
How It Works:
- Nutrient solution is delivered to the plants.
- Excess solution, which is not absorbed by the plants, drains away and is discarded (wasted).
- Fresh nutrient solution is prepared and supplied to the plants regularly.
Advantages:
- Nutrient Consistency: Plants always receive a fresh supply of nutrients, ensuring optimal growth conditions.
- Simplicity: These systems are generally simpler to design, install, and maintain.
- Reduced Risk of Pathogen Spread: Since the runoff is discarded, there is less risk of pathogens spreading throughout the system.
Disadvantages:
- Water and Nutrient Waste: Significant amounts of water and nutrients can be wasted, which is not environmentally friendly and can be more costly.
- Environmental Impact: Runoff can contribute to environmental pollution if not managed properly.
Recirculating System:
How It Works:
- Nutrient solution is delivered to the plants.
- Excess solution, which is not absorbed by the plants, drains back into a reservoir.
- The solution is filtered, adjusted for pH and nutrient concentration if necessary, and then reused in the system.
Advantages:
- Water and Nutrient Conservation: Significantly reduces water and nutrient waste, making the system more cost-effective and environmentally friendly.
- Efficiency: Maximizes the use of nutrients, reducing the need for frequent replenishment.
- Sustainability: Lower environmental impact due to minimal runoff.
Disadvantages:
- Complexity: Requires more sophisticated design, including filtration systems, monitoring equipment, and potentially automated control systems.
- Pathogen Risk: If not properly managed, recirculating systems can spread diseases and pathogens more easily.
- Nutrient Management: Requires regular monitoring and adjustment of nutrient concentrations and pH levels to maintain optimal conditions for plant growth.
Implementation Tips for a Recirculating System:
- Effective Filtration: Install filters, and possibly UV sterilizers to keep the nutrient solution clean and pathogen-free.
- Nutrient and pH Monitoring: Use automated systems to constantly monitor and adjust nutrient levels and pH to ensure optimal growing conditions.
- Regular Maintenance: Schedule regular maintenance for pumps, filters, and reservoirs to ensure the system operates smoothly.
- Backup Systems: Implement backup pumps and power supplies to prevent interruptions in nutrient delivery.
Summary:
- Drain-to-Waste System: Simpler and ensures fresh nutrients with each feeding but wastes water and nutrients, and can have higher environmental impact.
- Recirculating System: More complex and requires careful management but conserves water and nutrients, and is more environmentally sustainable.
The choice between these systems often depends on specific project goals, resources, and environmental considerations.
What is the greenhouse effect model?
The greenhouse effect model is a simplified representation of how the Earth's atmosphere interacts with sunlight and heat. It helps explain the phenomenon of the greenhouse effect, which is the process by which certain gases in the atmosphere trap heat and warm the Earth's surface.
Here is a basic outline of the greenhouse effect model:
Sunlight: The Sun emits shortwave solar radiation, primarily in the form of visible light and ultraviolet (UV) radiation, which reaches the Earth's atmosphere.
Absorption by the Earth: The Earth's surface absorbs a portion of the incoming sunlight, converting it into heat energy.
Greenhouse gases: Certain gases in the atmosphere, commonly known as greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and water vapor (H2O), absorb and re-emit some of the heat energy radiated by the Earth's surface.
Energy transfer: The absorbed heat energy is then re-radiated in all directions, including back towards the Earth's surface. This process is known as downward longwave radiation.
Greenhouse effect: The re-radiated energy increases the temperature of the Earth's surface and lower atmosphere, similar to how heat is trapped in a greenhouse. This warming effect is called the greenhouse effect.
Climate regulation: The greenhouse effect is essential for maintaining a habitable climate on Earth, as it helps regulate the planet's temperature by trapping a portion of the heat energy. Without it, the Earth would be much colder, and life as we know it would not be possible.
However, human activities, particularly the burning of fossil fuels and deforestation, have significantly increased the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. This enhanced greenhouse effect is leading to global warming and climate change, with potential adverse consequences for the planet's ecosystems and human societies.

Soy sauce is one of the most versatile condiments in any kitchen, especially in Asian cuisine. From marinades to dipping sauces, soy sauce brings out the natural umami in food and enhances both flavor and color. But with so many varieties available, how do you make the most of it—particularly when using Superior Light Soy Sauce?
The Role of Light Soy Sauce in Cooking
Superior Light Soy Sauce is known for its rich aroma, reddish-brown hue, and balanced saltiness. Unlike dark soy sauce, which is thicker and sweeter, light soy sauce is primarily used for seasoning rather than coloring. It’s perfect for quick stir-fries, steamed dishes, and even cold appetizers like tofu or salads. Add a splash during cooking to enhance the natural taste of ingredients without overpowering them.
Best Ways to Use Superior Light Soy Sauce
To bring out the best in your dishes, use Golden Label Superior Light Soy Sauce as a finishing touch. For example, drizzle it over blanched vegetables, steamed fish, or fried rice to elevate flavor instantly. It also works wonders as a dipping sauce base—just mix it with garlic, chili, or a touch of sesame oil. Chefs often prefer Superior Light Soy Sauce 1.9L packaging for commercial kitchens, thanks to its larger size, quality consistency, and cost-effectiveness.
Cooking Tips for Maximum Flavor
When using Superior Light Soy Sauce, timing matters. Add it towards the end of cooking to preserve its aroma and nuanced flavor. For marinades, combine it with ginger, garlic, and rice wine for a well-rounded base. Whether you're cooking meat, seafood, or vegetables, this type of soy sauce helps achieve that authentic taste found in restaurant-quality dishes.
Why Choose Our Superior Light Soy Sauce?
Our Superior Light Soy Sauce is brewed naturally using traditional methods, resulting in a complex yet smooth flavor profile. Whether it's the Golden Label Superior Light Soy Sauce for premium results or the convenient Superior Light Soy Sauce 1.9L for everyday use, our soy sauce offers consistent quality trusted by chefs worldwide. As a supplier dedicated to authentic flavor and food safety, we provide customizable packaging, global shipping, and responsive customer service to support both home cooks and professional kitchens.

Chicken powder makes food taste rich and delicious. It is made from dried chicken broth mixed with spices and seasonings. It helps you cook faster and makes meals better. Many people use it because it works in many recipes. By 2030, its market is expected to grow by 5.2% each year.
What Is Chicken Powder?
Definition and Key Ingredients
Chicken powder is a seasoning that adds a chicken-like taste to food. It is made by drying chicken broth and mixing it with other ingredients. This creates a fine powder that dissolves in liquids or blends into dry recipes.
Here are the main ingredients often found in chicken powder:
-
Dried chicken broth or chicken extract
-
Monosodium glutamate (MSG) to boost savory flavors
-
Salt and sugar for balanced taste
-
Spices like garlic, onion, or pepper for extra flavor
-
Maltodextrin to improve texture and thickness
-
Chicken fat for a richer flavor
-
Yeast extract, disodium inosinate, and disodium guanylate for stronger taste
Tip: MSG in chicken powder makes it taste more savory. Use it to create bold and tasty dishes.
These ingredients make chicken powder flavorful and useful for many recipes.
How It Differs from Chicken Bouillon and Stock
Chicken powder, bouillon, and stock may seem alike but are used differently. Knowing their differences helps you pick the right one for your dish.
|
Feature |
Chicken Powder |
Chicken Bouillon |
Chicken Stock |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Form |
Powder or granules |
Cubes or small granules |
Liquid |
|
Preparation |
Made from dried chicken broth |
Compressed chicken flavor with salt |
Made by simmering chicken and veggies |
|
Flavor Intensity |
Very strong and adjustable |
Strong but less flexible |
Mild and natural |
|
Convenience |
Easy to dissolve and store |
Simple to use but less versatile |
Needs time to prepare and refrigerate |
Chicken powder is easy to use and very flexible. Unlike bouillon, you can adjust its flavor strength. Compared to stock, it saves time but still tastes great. Use it for soups, marinades, or quick meals—it works for almost anything!
Benefits of Using Chicken Powder in Cooking
Boosts Savory and Meaty Flavors
Chicken powder makes food taste more savory and rich. It adds a "meaty" flavor to soups, sauces, and marinades. Monosodium glutamate (MSG) helps make meals even tastier. You can use chicken powder instead of extra spices or seasonings. Add it to stews or noodle dishes for bold flavors. Every bite will be full of delicious taste.
Easy and Saves Time
Chicken powder helps you cook faster and easier. You don’t need to simmer stock or marinate for hours. Studies show it saves time in the kitchen:
-
Pre-seasoned chicken cubes are quick to use.
-
They give the same flavor to every dish.
-
You don’t need extra steps to prepare meals.
Chicken powder is great for busy cooks. Mix it with water for broth or sprinkle it on food. It keeps meals tasty while saving time.
Works with Many Cuisines
Chicken powder fits into many types of cooking styles. It works well in Chinese, Italian, and Mexican recipes. Use it for hot pot broth or creamy pasta sauce. It also improves vegetarian dishes like dips and veggie soups. Chicken powder lets you try new flavors and improve old recipes.
Practical Uses of Chicken Powder
As a Stock or Broth Replacement
Chicken powder is a fast replacement for stock or broth. Homemade stock takes hours to make, but chicken powder dissolves quickly in water. It gives a rich and savory flavor to your meals. This makes it perfect for busy cooks who need quick solutions.
You can control the flavor strength by adjusting the amount used. Use less for a mild taste or more for a stronger flavor. This flexibility makes chicken powder great for soups, stews, and gravies. It offers the depth of homemade stock with added convenience, making it a kitchen favorite.
In Soups, Stews, and Sauces
Chicken powder boosts the savory taste in soups, stews, and sauces. It mixes well with other spices, creating a balanced flavor. Studies show that umami-rich chicken soup can improve appetite and nutrient absorption. It may also help reduce inflammation and ease cold symptoms, making it both tasty and comforting.
Here’s a table comparing sodium levels in different bouillons. It shows how chicken powder keeps flavor while lowering salt:
|
Bouillon Type |
Sodium (mg/100g) |
Salt Cut (%) |
Liked by Consumers |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Regular |
24,473 |
0 |
High |
|
Reduced 1 |
22,025 |
10 |
High |
|
Reduced 2 |
18,000 |
26 |
High |
|
Reduced 3 |
13,000 |
47 |
High |
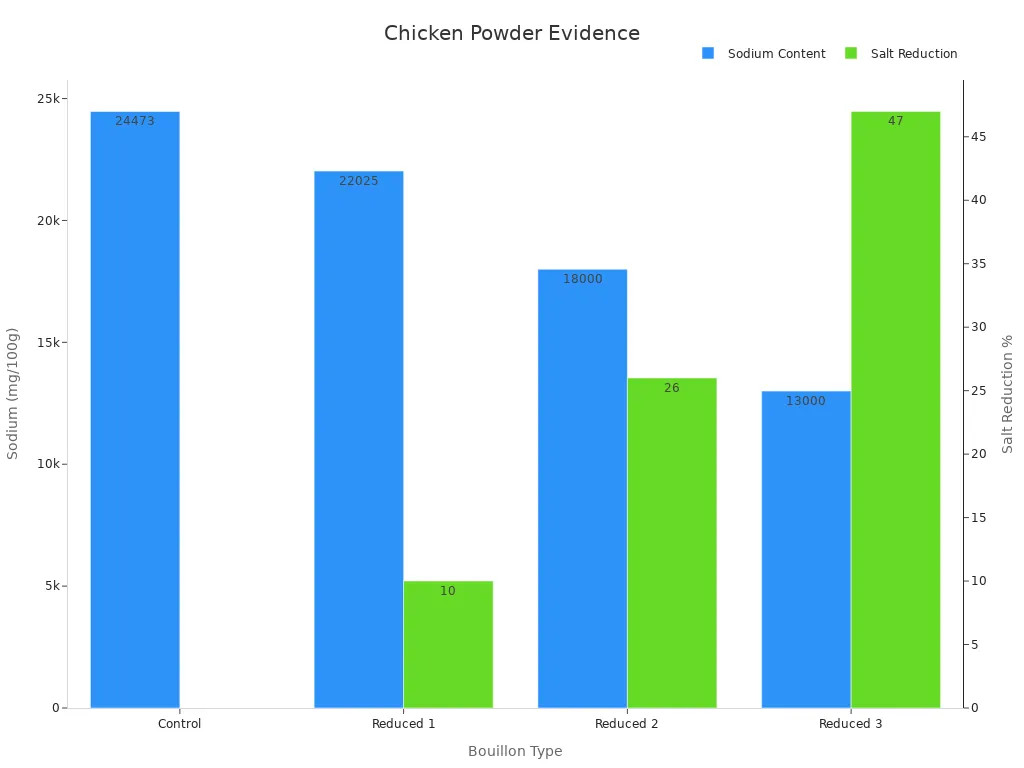
Using chicken powder balances flavor and health, making it a smart choice for cooking.
In Rice, Noodles, and Marinades
Chicken powder makes rice, noodles, and marinades taste better. Add a teaspoon to rice water for a subtle flavor boost. Sprinkle it into noodle broth or sauce for a richer taste.
In marinades, chicken powder enhances the flavor of meats. Mix it with garlic, onion, and pepper for a tasty marinade. It works well in many cuisines, like Chinese stir-fried noodles or Italian risottos.
In Dips, Spreads, and Vegetarian Meals
Chicken powder isn’t just for meat dishes. It improves vegetarian recipes too. Add a pinch to dips like hummus or guacamole for extra flavor. It blends well with other seasonings for a balanced taste.
For vegetarian soups and stews, chicken powder adds umami flavor. It also works in roasted vegetable dishes, enhancing their natural sweetness. Its versatility makes it a must-have for all types of cooking.
Comparing Chicken Powder to Alternatives
Chicken Powder vs. Chicken Bouillon
Chicken powder and bouillon cubes are similar but not the same. Bouillon cubes are compact and salty, while chicken powder is fine and dissolves quickly. Bouillon has a fixed flavor, but chicken powder lets you adjust taste by using more or less.
Some bouillon brands have unwanted additives, making chicken powder a cleaner choice. Homemade stocks and broths are healthier but take time to prepare. Chicken powder is a quick and easy option for busy days.
Tip: Add chicken powder to soups or stews for fast, tasty meals without losing quality.
Chicken Powder vs. Chicken Essence
Chicken powder and chicken essence are made differently and used for different purposes. Chicken essence is heated and filtered to create a clear, nutrient-rich liquid. Chicken powder has dried chicken and small particles, making it better for dry recipes.
|
Aspect |
Chicken Essence |
Chicken Powder |
|---|---|---|
|
Pasteurization |
Heated to remove harmful bacteria |
Usually not pasteurized |
|
Filtration |
Filtered for a clear liquid |
May include small particles |
|
Ingredients |
Made from chicken, water, and seasonings |
Includes dried chicken and spices |
|
Nutritional Value |
High in vitamins and minerals |
Varies by brand |
Chicken essence is great for nutrition, while chicken powder works in many recipes. Both add flavor, but chicken powder’s spices make it more useful for everyday cooking.
Chicken Powder vs. Homemade Stock
Homemade stock tastes fresh and mild but takes time to make. Chicken powder is faster and adds a rich, savory flavor without hours of cooking. Bone broth, a type of stock, is more nutritious than chicken powder or bouillon.
Store-bought concentrates are like bouillon but lack homemade stock’s depth. Chicken powder is a good middle ground, offering strong flavor and convenience. For busy cooks, it’s a handy substitute. Add fresh spices to make it taste closer to homemade stock.
Nutritional Considerations and Potential Downsides
Nutritional Value of Chicken Powder
Chicken powder is an easy way to make meals tastier. It also adds some protein, which helps muscles stay strong. The amount of protein depends on the brand you use.
Here’s a table showing how protein levels affect body fat:
|
Study |
Protein Level |
Effect on Body Fat |
|---|---|---|
|
Kassim and Suwanpradit |
23% to 20% CP |
More belly fat |
|
Collin et al. |
Low-protein vs Normal |
More belly fat |
|
Yalçin et al. |
19.2%, 16.6%, 15.5% |
More total body fat |
|
Yalçin et al. |
26.6%, 23.5%, 20.7% |
Less total body fat |
|
Jlali et al. |
17% to 23% CP |
Less belly fat |
This table shows higher protein can lower body fat. Picking chicken powder with more protein can help you eat healthier without losing flavor.
Sodium Content and Health Implications
Chicken powder has sodium, which makes food taste better. Sodium is important for your body but too much is harmful. Eating too much sodium can cause high blood pressure. For example, turkey bacon has over 2000 mg of sodium per 100 g. Fresh chicken has less than 100 mg.
Bouillon and store-bought broths also have lots of sodium. Chicken powder is a tasty option, but watch your sodium intake. Too much sodium can lead to heart problems or strokes. Use it carefully to stay healthy.
Moderation and Sensitivity Awareness
Using chicken powder in small amounts is the best choice. This way, you avoid too much sodium or other additives. If you’re sensitive to MSG or certain spices, check the label first. Some people may feel mild side effects from these ingredients. Start with a little and adjust as needed.
Mixing chicken powder with fresh foods keeps meals healthy and flavorful. Watch your portion sizes and ingredient sensitivities. This lets you enjoy chicken powder’s taste without risking your health.
Tips for Choosing and Storing Chicken Powder
Recommended Brands
Pick chicken powder from brands with good quality. Choose products made with natural chicken extract. Avoid powders with unnecessary additives. Look for clear ingredient lists and food safety certifications. Trusted spices and seasonings brands offer better flavor and health benefits. These brands help make your dishes tasty and safe.
Proper Storage Techniques
Store chicken powder properly to keep it fresh longer. Use airtight containers to stop moisture from causing clumps or spoilage. Keep it in a cool, dry place away from sunlight. If the package is resealable, close it tightly after each use. For long storage, use UV-resistant containers to protect its quality.
Do Seasonings Expire?
Yes, seasonings can expire. The expiration of seasonings depends on storage and packaging. Old chicken powder may lose its smell, taste, and strength. Watch for these signs that your seasonings have expired:
-
Clumps or faded color
-
Weak smell or stale aroma
-
Less flavor when cooking
Good packaging helps seasonings last longer.
|
Evidence Description |
Impact on Food Safety and Shelf Life |
|---|---|
|
Airtight packaging stops moisture |
Prevents clumps, spoilage, and germs |
|
Secure seals stop oxidation |
Keeps flavor fresh |
|
UV-resistant containers block light |
Protects ingredients from damage |
|
Tight sealing keeps aroma inside |
Maintains seasoning's appeal |
Follow these tips to keep your chicken powder fresh and flavorful.
Chicken powder makes cooking easier and tastier. It adds strong flavors and helps you cook faster. You can use it in many recipes to improve old dishes or try new ones.

Pro Tip: Try chicken powder in various cuisines. It can bring new and exciting flavors to your meals.
Natural sweeteners are sweet substances extracted from natural plants, such as glucose, beet extract, etc. Artificial sweeteners are synthetics produced by chemical synthesis or fermentation, such as aspartame, saccharin and maltodextrin. The difference between the two is mainly reflected in the following aspects:
Flavor
Natural sweeteners: taste closer to the taste of sugar .
Artificial sweeteners: taste sweeter, similar to the taste of chemicals, some people even do not like it, but it is sweeter than natural sweeteners .
Calories
Natural sweeteners: most are low or no calories, but similar to sugar.
Artificial sweeteners: have no calories at all, which makes it a popular choice for patients who want to lose weight, control diabetes, etc .
Safety
Natural sweeteners: are safe and have essentially no side effects .
Artificial sweeteners: are considered by some to have potential health risks, such as carcinogenic, wheezing, headache and other side effects, but there are no clear studies proving that they are harmful to health .
Application Scenarios
Natural sweeteners: suitable for natural foods, beverages, special diets and other occasions, which are friendlier to health .
Artificial sweeteners: Suitable for sugar-free, low-sugar, low-calorie foods, but need to pay attention to lead to sweet taste preference and appetite disorders and other issues .
Overall, natural sweeteners and artificial sweeteners have their own advantages and disadvantages, and should be chosen for use according to specific circumstances. For the general population, natural sweeteners can be used in moderation; for special populations such as those on a diet or suffering from diabetes, artificial sweeteners can be considered. However, no matter which kind of sweetener, should be used in moderation, healthy diet is the key .

Aspartame is a widely used low-calorie sweeteners composed of aspartic acid and phenylalanine. Moderate intake of aspartame is generally considered safe, but there may be some hazards associated with prolonged high intake or for specific populations:
Allergic reactions
Phenylalanine can cause allergic reactions, which are especially dangerous for people with asthma and hay fever. An allergic reaction may manifest itself in symptoms such as headache, facial heat, rash, shortness of breath and, in severe cases, may lead to shock and death.
Increased risk of disease
Studies have shown that phenylalanine negatively affects the gastrointestinal tract, leading to gastrointestinal inflammation and gut microbial dysbiosis. If ingested consistently, it may increase the risk of diseases such as cancer, diabetes, and obesity.
Affects the nervous system
Phenylalanine is broken down in the body into phenylacetone, which can affect the synthesis and release of neurotransmitters, leading to neurological symptoms such as headaches, memory loss, and insomnia.
Phenylalanine, a metabolite of aspartame, may compete with other substances when passing through the blood-brain barrier, thereby interfering with neurotransmitter transmission and possibly inducing the development of migraines, especially when ingested in excess, which may lead to neurological damage.
It has been suggested that aspartame may cross the blood-brain barrier, altering amino acid ratios in the brain and interfering with neurotransmitter transmission, which may increase the incidence of brain disorders and may also affect memory.
Hazards to Specific Populations
People with phenylketonuria
These patients lack the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase, which converts phenylalanine into a harmless substance. The phenylalanine in aspartame further increases the concentration of phenylalanine in the blood, leading to the accumulation of phenylalanine in the body, which can exacerbate the clinical symptoms, and may also lead to brain damage and weakening of the intellect.
Other possible harms
Low immunity: If the elevation of phenylalanine is triggered due to excessive intake of aspartame, it may affect the stabilization of amino acid levels in the body, which is more likely to make the human body develop low immunity.
Other potential effects: It may also have an effect on gut microbes, may lead to liver problems, and may have an effect on bone health.
Technological maturity
Erythritol has been industrialized for about 10 years, while Allulose(D-allulose,D-Psicose) Sugar only has a history of 3 to 5 years in China, so in terms of technological maturity, Erythritol is relatively higher.
Raw material difference
Arotonose is made directly from crystallized fructose, while the direct raw material of erythritol is glucose.
Characteristic and Function Differences
Source and nature: alloxyketose is a rare monosaccharide that exists naturally in nature but in a very small amount; erythritol is a natural sweetener, generally extracted from natural plants or produced by fermentation .
Taste: The sweeteners and taste of Aloe Ketone Sugar is quite similar or close to that of sucrose, with a soft and delicate taste, mild and delicate sweetness, and no bad taste during and after consumption; Erythritol is moderately sweet, with a clear sense of coolness.
Calories and health effects: both calories are much lower than sucrose, but in addition to the role of sugar substitutes, Aloe Ketone Sugar also helps diabetic patients to lower the role of glucose, and other sugar substitutes do not have the effect of baking.
Market and application differences
Market situation: The U.S. FDA announced that Alozone Sugar is not labeled in the nutrition label of added sugar and total sugar, so its added amount is not calculated in these two categories, which lays a policy foundation for the large number of applications of Alozone Sugar in food products, especially in sugar-free and sugar-reduced products. However, at present, Alozone Sugar has not been widely sold in the country; erythritol market application has been more widely .
Capacity utilization: Bowling Green some production lines due to oversupply, the current utilization rate may reach more than 100%, while constantly expanding the capacity of the best-selling products, there are also individual production line utilization rate of 70% -80%, depending on the demand for specific products . But in general, the capacity utilization rate of two products of different enterprises varies according to the market demand.

- Buddha Jump Over the Wall1
- Canned Abalone2
- Canned Turtle Soup1
- Edible Bird's Nest2
- Frozen Foods1
- Frozen Seafood8
- Jelly/Pudding Applications1
- Meat Product Applications2
- Others Applications5
- Plant-based meat Product Applications1
- SURIMI2
- Soft Candy1
- Soft Candy Applications4
- bottle1
- can end2
- packaging film2
- tableware3